最近公司项目没那么紧,然后心态有点放松了,算有点飘吧(开玩笑),然后想写点东西给自己打打鸡血,让心态沉稳淡定下来,想想公司基本都是用Vue在开发项目,然后想到Vue的对头React,还是写篇他们的比较文章吧,其实还想说Angular的,但是Angular2.0出来后,我就基本用的很少了,虽然也有Angular脚手架(angular-cli),但是需要使用ts语法,确实让人有些不习惯。所以这次就比较下React和Vue的区别吧,这篇文章主要站在React的角度去比较Vue, 接下来进入正题……。
框架简介
说到这些强大的web前端框架,主要是用来开发单页(SPA)应用,可以理解为一个核心、三个主要组成部分;核心思想为双向数据绑定,三个主要组成:组件化、路由系统和数据传递。掌握这些基本可以用框架开发了,但是项目想搭建的更符合自己的风格,开发更得心应手,那就需要深刻了解Webpack了,因为基本常用的前端脚手架都是以webpack为基础搭建的,了解了它,插件的引入,模块化加载,预编译等等都会变得那么简单,不会太依赖脚手架了。
历史背景
React起源于FaceBook的内部项目,因为该公司对市场上所有 JavaScript MVC 框架,都不满意,就决定自己写一套,用来架设Instagram 的网站。做出来以后,发现这套东西很好用,就在2013年5月开源了。
Vue的作者是尤大大(尤雨溪),简直是国人的骄傲,造福了我们这些前端开发工作者,官方文档更是介绍的非常详细,而且还是中文啊,相对于React或者Angular是更容易上手的,给尤大大点个赞。
渲染函数
渲染函数是Vue和React模板渲染的底层,React会将JSX,Vue会将模板template转化为渲染函数。createElement返回的是VNode(虚拟dom),里面包含了DOM节点的信息。
React
const element = (
<h1 className="greeting">
Hello, world!
</h1>
);
const element = React.createElement(
'h1',
{className: 'greeting'},
'Hello, world!'
);
// React.createElement() 这个方法首先会进行一些避免bug的检查,之后会返回一个类似下面
// 注意: 以下示例是简化过的(不代表在 React 源码中是这样)
const element = {
type: 'h1',
props: {
className: 'greeting',
children: 'Hello, world'
}
};
Vue
<h1 class="greeting">
Hello, world!
</h1>
Vue.component('HComponet', {
render: function(createElement) {
return createElement('h1', {
class: {
greeting: true
},
domProps: {
innerHTML: 'Hell0, world!'
}
})
}
})
生命周期
React和Vue的生命周期这里不做详细比较,基本是相同的,Vue的Created、mounted、beforeUpdate、updated、beforeDestroy等对应React的componentWillMount、componentDidMount、componetWillUpdate、componentDidUpdate、componentWillUnmount。借用官网的图片如下。。。
React
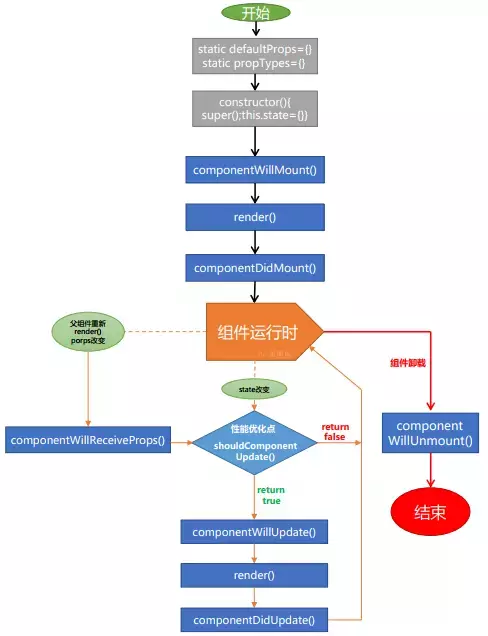 Vue
Vue
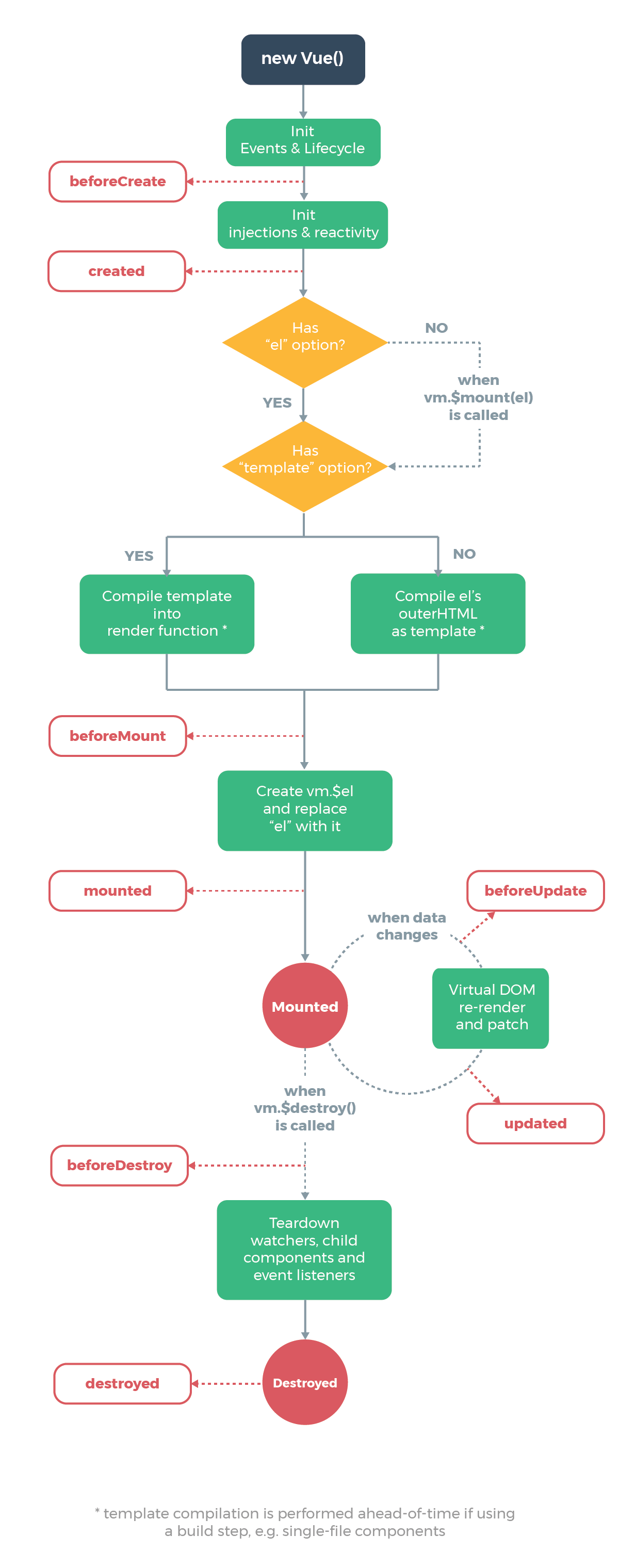
组件化
组件化思想,使代码变得高效、高复用以及容易理解。组件可以嵌套,循环还可以条件判断等等,代码讲究的是高内聚低耦合,我想组件化就是为它而生啊。
React
函数就是组件,注意函数名大写,因为组件都是大写字母开头
function WarnComponent(props) {
// 隐藏和展示组件
if (!props.warn) {
return null;
}
return (
<div className="warning">
Warning!
</div>
)
}
React的组件主要用JSX语法替代了JavaScript,虽然不一定使用JSX,但是它执行快,类型安全以及编写模板高效快速的特点,不得不使你喜欢,甚至使用React就会依赖上它,虽然JSX入手有点困难,习惯了还是很容易理解的。原理就是JSX构建的组件对象,实现一个render()的方法,并且根据输入的数据返回相应的结果,render()方法通过this.props访问这些输入的数据。附上一段JSX的代码
import React from 'react'
import axios from '@/api'
import HomeHeader from '@/components/homeHeader'
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
import { getMeetingData } from '@/reduxs/handle'
import './index.scss'
const mapStateToProps = state => {
return {
value: state
}
}
// mapDispatchToProps:将dispatch映射到组件的props中
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch, ownProps) => {
return {
getMeetingDatas (data) {
dispatch(getMeetingData(data))
}
// 上行代码相当于
/*dispatch(( dispatch, getState ) => {
axios.meeting()
.then(res =>
dispatch({type: 'GET_MEETING_DATA', data: res.data})
})
)*/
}
}
class Meeting extends React.Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {
}
}
// 生命周期函数
componentDidMount() {
this.props.getMeetingDatas()
}
render(){
return (
<div className='meeting-page'>
<HomeHeader title={'会议页面'}/>
会议页面{this.props.value.visibilityFilter}
</div>
)
}
}
export default connect( mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps )(Meeting)
);
Vue
Vue的组件化就简单的多了,一般采用模板。
<template>
<div class="warning">
Warning!
</div>
</template>
通过import组件到指定页面,然后components注册就可以在template模板中使用了,至于嵌套,循环组件等,就需要自己去想如何更高效的利用这些组件了。
路由系统
路由系统它们两者写法有很大区别,但是据React官网介绍,可以写成与Vue类似的结构,但是一般不推荐。
React
React的路由其实也是一个组件,这里主要讲react-router3,官网介绍的比较详细,我这里就不再详细讲解,使用的时候需要调用this.props.children到指定位置,表示组件的所有子节点。附上路由代码
import React from 'react'
import { Router, Route, IndexRoute, IndexRedirect, Redirect, browserHistory } from 'react-router'
import App from '../App'
import Login from '../pages/login'
import Home from '../pages/home'
import Main from '../pages/home/main'
import Meeting from '../pages/home/meeting'
import Device from '../pages/home/device'
import Users from '../pages/home/users'
import NoFound from '../pages/noFound/index'
const routes = (
<Router history={browserHistory}>
<Route path="/">
<IndexRedirect to="login"/>
<Route path="login" component={Login}/>
<Route path="home" component={Home}>
{/* <Redirect to="home/main"/> */}
<IndexRedirect to="main"/>
{/* <IndexRoute component={Main}/> */}
<Route path="main" component={Main}/>
<Route path="meeting" component={Meeting}/>
<Route path="device" component={Device}/>
<Route path="users" component={Users}/>
{/* <Route path="main" component={Main}/> */}
</Route>
</Route>
<Route path="/noFound" component={NoFound}/>
<Redirect from="*" to="/noFound" />
</Router>
);
export default routes
// 注意:需要引入到组件中使用
Vue
Vue 的路由就是new Router({}),通过<router-view/>标签来使用,附上代码
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Login',
component: Login
},
{
path: '/register',
name: 'Register',
component: Register
},
{
path: '/system',
name: 'System',
component: System
}
]
})
至于那些高阶动态路由,嵌套路由,路由守卫就不一一介绍了 官网介绍的很详细。
数据传递
props传参对比
React
<!-- 父传子 -->
<Child handle={[参数]}/>
<!-- 子传父 -->
<Child handle={[参数]}> // 参数 ==》 callback函数
是不是感觉是一样的,只不过父传子有点技巧,使用callback传参,即传递给子组件的是callback函数,子组件调用callback(val),父组件取val,callback原理就不多讲了,其实用的方法就一个props,如果你想通过Props进行组件传参,那么callback是核心思想,并且它能传递函数,组件,对象、数组等任何类型参数。
Vue
<!-- 父传子 -->
<Child data="[参数]"/> // props 方法
<!-- 子传父 -->
child.vue
this.$emit('handle', val) // vm.$emit('handle', val)
Vue就遵循自己的方法,例子显而易懂,这里不做多讲解。
(Redux VS Vuex)
React
React数据分三步走:action定义变量,即dispatch事件;reducer写逻辑部分,改变state内容;store即创建store,核心为combineReducers() 和createStore(),最后export导出到需要地方
const todoApp = combineReducers({
visibilityFilter,
todos,
getMeetingData
})
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
import { applyMiddleware, createStore } from 'redux'
import todoApp from './reducers'
// 初始化state方法二 权重最高的初始化
let store = createStore(todoApp, {visibilityFilter: 'cc', todos: [{name: 'vinter', property: 'wealthiness'}]}, applyMiddleware(thunk))
export default store
上面我使用了中间件redux-thunk和applyMiddleware,用来异步请求接口,dispatch的函数会接受dispatch作为参数
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch, ownProps) => {
return {
getMeetingDatas (data) {
dispatch(getMeetingData(data))
}
// 上行代码相当于
/*dispatch(( dispatch, getState ) => {
axios.meeting()
.then(res =>
dispatch({type: 'GET_MEETING_DATA', data: res.data})
})
)*/
}
}
如果是不复杂的项目不建议使用Redux,因为构建redux反而会让数据凌乱起来,所以请遵循下面:
如果你不知道是否需要 Redux,那就是不需要它。
只有遇到 React 实在解决不了的问题,你才需要 Redux 。
以下情况可以考虑使用
- 用户的使用方式复杂
- 不同身份的用户有不同的使用方式(比如普通用户和管理员)
- 多个用户之间可以协作
- 与服务器大量交互,或者使用了WebSocket
- View要从多个来源获取数据
Vue
Vue结构就比较简单,四大金刚:state文件,状态初始化;action文件,dispatch触发,异步请求在这里执行;mutation文件,直接改变state状态,触发页面更新;getter文件,这个文件方便各页面接受数据的,四大金刚对应的辅助函数 (mapState, mapActions, mapMutations, mapGetters)
import { mapState, mapGetters, mapActions, mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapGetters(['fn1', 'fn2'])
// ...mapGetters({
fnName1: 'fn1',
fnName2: 'fn2'
})
}
}
最后附上我的React的Demo地址, 主要通过create-react-app脚手架搭建的。这里Vue的Demo就不展示了,因为通过vue-cli可以很快速的搭建起来。
React的组合和属性 VS Vue插槽和路由
React React组件组合
function SideBar(prop) {
return <div>
{prop.header}
{prop.footer}
{prop.children}
</div>
}
function Footer(prop) {
return <div>{prop.footer}</div>
}
class Parent extends Component {
render() {
return (
<SideBar
header={ <div>hello, world!</div> }
footer={ <Footer footer='footer'/> }
>
<div>child</div>
</SideBar>
)
}
}
React的路由渲染
function Bar(prop) {
return (
<div>
{prop.children}
</div>
)
}
Vue Vue的插槽
// parent
<side-bar>
<template #header='{headerData}'>
<div></div>
</template>
<template #footer='{footerData}'>
<div></div>
</template>
</side-bar>
// son
<slot name='header' :headerData="'header'"/>
<slot name='footer' :footerData="'footer'"/>
Vue的路由渲染
<router-view/>
从上面可以比较出来,React的核心就是利用函数传参和组建的属性来进行组合嵌套,请记住,组件可以接受任意元素,包括基本数据类型、React 元素或函数。Vue则是利用插槽的语法。
Life sucks when you’re ordinary.